How can a Lone Worker App Protect Your People in High-Risk Situations?
Lone workers face greater risks than those who have co-workers nearby. Without support they may be unable to get immediate assistance in case of injury, incapacity or another type of emergency situation.
Why do I need a lone worker app?
A work alone safety device, such as a lone worker app, ensures employees have a direct line to help. But what happens when workers face unexpected situations that place them at even greater risk?
- A healthcare worker may need to care for an aggressive, volatile patient
- A lab worker may need to work after hours with hazardous equipment or chemicals
- A truck driver or courier may need to drive on an isolated stretch of road in treacherous weather conditions
Even if no obvious risk is present, sometimes people on their own feel a real sense of unease about going into a situation. They want a little boost of protection to help them carry on with their jobs. Or perhaps they just want to take charge and make an important decision regarding their own safety.
How can lone workers get more control?
For most people, lone worker safety policies are agreed on once, and then left to run. Schedules, check-in frequencies, and hazard assessments just seem to happen in the background without a lot of additional input from the lone worker.
In high-risk situations however, giving your team a lone worker app is not just about providing additional assurance that help is readily available. On one level, it’s about giving them control of their environment and managing the risks associated with it. Sometimes this comes down to training, experience, and risk management. Equally, it’s also about giving workers control of their own emergency response.
High-risk features act as a lone worker safety line
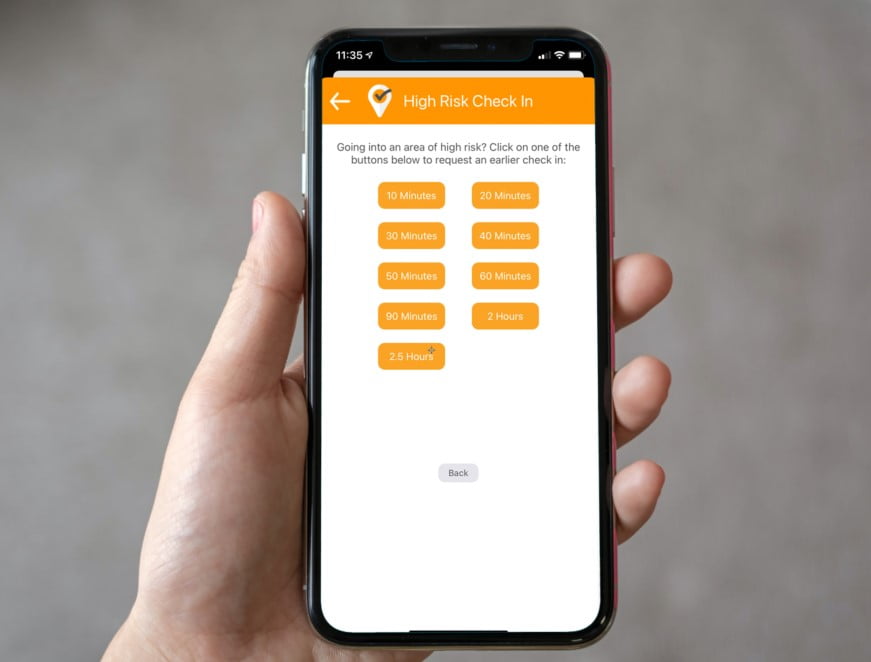
If a worker ever finds them self in a scenario like one of those mentioned earlier, they need the power to take control and switch on the high-risk safety features of a professional grade lone worker app.
With a well designed lone worker solution, they can safeguard themselves by checking in before going into a high risk situation, sending a short message or voicemail to their monitor explaining exactly what is about to happen and then shortening their next check-in time to something appropriate for the situation. Anything from 10 minutes to an hour usually does the trick. Of course, should a worker need immediate assistance, the safety app must let them send an instant call for help.
What happens if a lone worker misses a check-in or calls for help?
If a worker fails to check in or uses the help button, their monitor(s) need to be notified immediately. Good systems let you do this in a number of ways. For example, monitors can be notified online, with a text message, WhatsApp, an email, by phone, or any combination, whatever works best for them.
Once the monitor is notified, they can carry out the appropriate escalation procedure to resolve the situation as quickly and safely as possible.
If you’re looking to give your team this kind of assurance, why not explore these features — and more — with Ok Alone’s free 7-day trial. Most people are up and running in 10 minutes or less and there’s no obligation or credit card information required.
Curious about how much it will cost you? Try our pricing calculator to find out – Ok Alone pricing proposal
Book a Demo Today
Alternatively, get a free trial of the app
Want to try OK Alone? Click the button below and enter your details. It's free and no credit card is required.





